The Akash Provider is a modular service that connects Kubernetes clusters to the Akash Network, enabling providers to bid on deployment orders and serve tenant workloads.
Architecture Components
The provider service consists of five main components that work together:
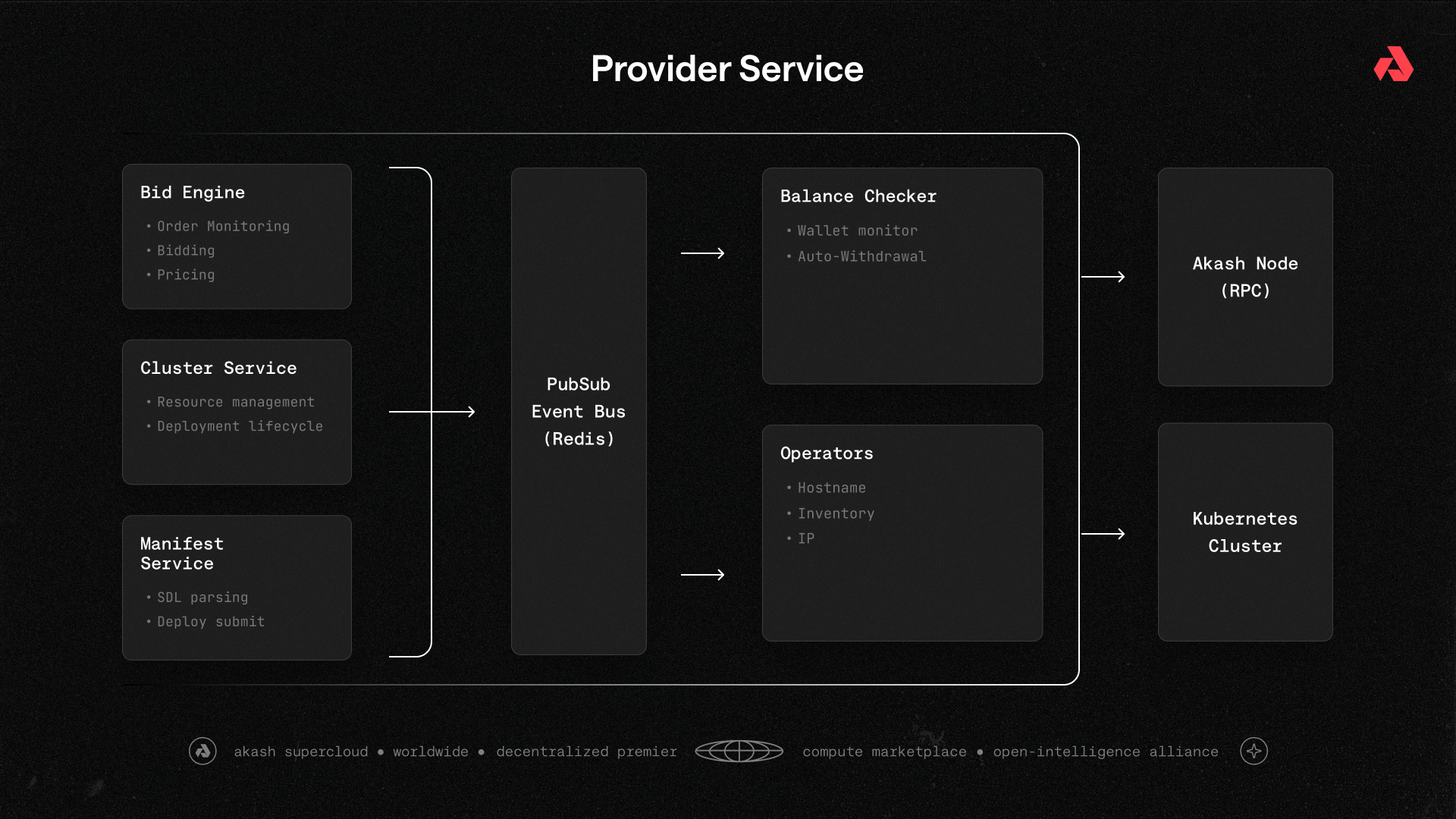
Core Services
1. Bid Engine Service
Purpose: Monitors the Akash blockchain for new deployment orders and decides whether to bid.
Responsibilities:
- Subscribes to
EventOrderCreatedevents from the blockchain - Evaluates orders against provider attributes and available resources
- Calculates bid prices using the configured pricing strategy
- Submits bids to the blockchain
- Manages the lifecycle of active orders
Key Features:
- Concurrent order processing
- Resource reservation before bidding
- Configurable pricing scripts (shell or scale-based)
- Provider attribute matching
- Automatic bid timeout handling
Code Location: /bidengine/service.go
2. Cluster Service
Purpose: Manages Kubernetes cluster resources and deployment lifecycle.
Responsibilities:
- Inventory Management - Tracks available cluster resources (CPU, GPU, memory, storage)
- Resource Reservation - Reserves resources for bids before they’re won
- Deployment Management - Creates and manages Kubernetes deployments for active leases
- Hostname Service - Manages custom hostnames and ingress routing
- Monitoring - Tracks deployment health and resource usage
Key Features:
- Real-time resource inventory tracking
- Support for GPU resources (NVIDIA)
- Persistent storage integration (Rook-Ceph)
- IP lease management (via MetalLB)
- Auto-scaling and resource adjustment
- Multi-tenancy isolation
Code Location: /cluster/service.go
3. Manifest Service
Purpose: Receives and processes deployment manifests (SDL) from tenants.
Responsibilities:
- Accepts manifest submissions via gRPC API
- Validates SDL syntax and resource requirements
- Pairs manifests with active leases
- Emits
ManifestReceivedevents for cluster service - Manages manifest lifecycle (submit, update, delete)
Key Features:
- SDL validation and parsing
- Hostname requirement validation
- Manifest versioning
- Watchdog for missing manifests
- Timeout handling for manifest submission
Code Location: /manifest/service.go
4. Operators
Purpose: Kubernetes operators that extend cluster functionality.
Hostname Operator
- Manages custom hostname assignments
- Creates Kubernetes Ingress resources
- Integrates with ingress controllers (Ingress-NGINX, Traefik)
- Handles hostname conflicts and validation
Inventory Operator
- Discovers cluster resources (CPU, GPU, storage)
- Tracks resource availability in real-time
- Supports hardware feature discovery
- Integrates with NVIDIA Device Plugin for GPUs
IP Operator
- Manages IP address leases
- Integrates with MetalLB for IP allocation
- Handles IP assignment and release
- Supports static IP requirements
Code Location: /operator/
5. Balance Checker
Purpose: Monitors provider wallet balance and triggers auto-withdrawals.
Responsibilities:
- Periodically checks provider account balance
- Withdraws accumulated earnings when threshold is met
- Ensures provider has sufficient funds for transactions
- Publishes balance events to the event bus
Code Location: /balance_checker.go
Communication & State Management
Event Bus (PubSub)
All services communicate via a Redis-backed publish-subscribe event bus. This enables:
- Loose Coupling - Services don’t directly depend on each other
- Event-Driven Architecture - Services react to events (orders, leases, manifests)
- State Synchronization - Services publish status updates
- Scalability - Services can be scaled independently
Key Event Topics:
akash.provider.cluster.status- Cluster resource updatesakash.provider.bidengine.status- Active order countakash.provider.manifest.status- Manifest processing statusakash.provider.inventory.status- Resource availability
Blockchain Events
The provider subscribes to Akash blockchain events:
EventOrderCreated- New deployment ordersEventLeaseCreated- Lease awarded to providerEventLeaseClosed- Lease terminated
Lifecycle Management
Each service implements lifecycle management using go-lifecycle:
- Initialization - Service starts and initializes resources
- Running - Service processes events and handles requests
- Shutdown - Graceful shutdown on error or termination signal
- Done - Cleanup complete, service stopped
Service Flow
1. Order Processing Flow

2. Deployment Flow

3. Lease Termination Flow

API Interfaces
gRPC API (Port 8444)
The provider exposes a gRPC API for:
- GetStatus - Provider status and resource availability
- ValidateGroupSpec - Pre-validate deployment requirements
Proto Definition: pkg.akt.dev/go/provider/v1
REST API (Port 8443)
The provider exposes a REST API for:
- Status - JSON status endpoint
- Manifest Submission - SDL upload endpoint
- Lease Management - Query lease details
Gateway: /gateway/rest/
Configuration
Provider configuration is managed via:
- Environment Variables - Basic settings (chain ID, keyring, etc.)
- provider.yaml - Provider attributes, pricing, features
- price_script.sh - Custom pricing logic (shell script)
Key Configuration:
# Attributesattributes: - key: host value: akash
# Pricingbidpricestoragescale: 1.0bidpricecpuscale: 1.0bidpricememoryscale: 1.0
# Featuresdeployment_ingress_static_hosts: truedeployment_ingress_domain: provider.example.comMonitoring & Observability
Prometheus Metrics
The provider exposes Prometheus metrics on port 8443:
provider_order_manager- Active orders being trackedprovider_deployment_manager- Active deploymentsprovider_manifest_manager- Manifests being processedprovider_order_handler- Order processing counters
Logs
Structured logging with configurable levels:
debug- Detailed service operationsinfo- Important events (orders, leases, deployments)error- Failures and exceptions
View Logs:
kubectl -n akash-services logs -l app=akash-provider --tail=100 -fHigh Availability
While the provider service itself runs as a single instance (StatefulSet), the underlying services support HA:
- Kubernetes Control Plane - Can be deployed in HA configuration (3+ nodes)
- Redis - Can be deployed in HA mode with Sentinel
- Ingress Controllers - Run as DaemonSets across all nodes
- Storage - Rook-Ceph provides distributed, redundant storage
Security
mTLS (Mutual TLS)
Provider services communicate with the blockchain using mTLS for authentication:
- Provider certificate stored in Kubernetes secret
- Automatic certificate rotation before expiry
- Certificate validation against Akash CA
Kubernetes RBAC
The provider uses service accounts with minimal RBAC permissions:
- Create/delete namespaces
- Manage deployments, services, ingress
- Read/write ConfigMaps and Secrets
- Access to CRDs (manifests, provider hosts)
Tenant Isolation
Each deployment runs in an isolated namespace with:
- Network policies (optional)
- Resource limits (CPU, memory, storage)
- No privileged containers by default
- Separate service accounts
Related Documentation
- Bid Engine - Detailed bidding logic
- Cluster Service - Resource management
- Manifest Service - SDL processing
- Operators - Kubernetes operators