An Akash Provider leases compute to users launching new deployments. Follow the steps in this guide to build your own provider.
This guide uses a single Kubernetes control plane node.
Overview and links to the steps involved in Akash Provider Build:
- Prerequisites of an Akash Provider
- Kubernetes Configurations
- Export Provider Wallet
- Helm Installation on Kubernetes Node
- Domain Name Review
- Hostname Operator Build
- Inventory Operator Install
- Provider Build via Helm Chart
- Provider Bid Customization
- Ingress Controller Install
- Firewall Rule Review
- Disable Unattended Upgrades
- Provider Whitelisting (Optional)
- Extras
STEP 1 - Prerequisites of an Akash Provider
NOTE - the commands in this section and in all remaining sections of this guide assume that the
rootuser is used. For ease we suggest using therootuser for the Kubernetes and Akash Provider install. If a non-root user is used instead, minor command adjustments may be necessary such as usingsudocommand prefixes and updating the home directory in command syntaxes.
Akash Wallet
Placing a bid on an order requires a 0.5 AKT deposit placed into collateral per bid won. If the provider desired 2 concurrent leases, the provider’s wallet would need minimum funding of 1 AKT.
As every deployment request bid requires 0.5 AKT to be deposited in the escrow account, it’s always good to have more so your provider can keep bidding. If your provider is ready to offer 10 deployments, then it’s best to have .5 x 10 = 5 AKT and a little more to make sure provider can pay the fees for broadcasting the transactions on Akash Network.
The steps to create an Akash wallet are covered in the following documentation sections:
Kubernetes Cluster
A full Kubernetes cluster is required with outbound internet access and be reachable from the internet.
If you need assistance in building a new cluster, visit the Kubernetes Cluster for Akash Providers guide.
RPC Node
Akash Providers need to run their own blockchain RPC node to remove dependence on public nodes. This is a strict requirement.
We have recently released documentation guiding thru the process of building a RPC node via Helm Charts with state sync.
CPU Support
Only x86_64 processors are officially supported by Akash for provider Kubernetes nodes at this time. This may change in the future and when ARM processors are supported it will be announced and documented.
Custom Kubernetes Cluster Settings
Akash Providers are deployed in many environments and we will make additions to these sections as when nuances are discovered.
Disable Search Domains
Overview
In this section we perform the following DNS adjustments:
Set Use Domains to False
- Set
use-domains: falseto prevent the possibility of systemd’s DHCP client overwriting the DNS search domain. This prevents a potentially bad domain served by the DHCP server from becoming active. - This is a common issue to some of the providers which is explained in more detail here
Set Accept RA to False
- Set
accept-ra: falseto disable IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) as the DNS search domain may still leak through if not disabled. - Potential issue this addresses is explained in more detail here
Create Netplan
NOTE - the DNS resolution issue & the Netplan fix addressed in this step are described here
Apply the following to all Kubernetes control plane and worker nodes.
IMPORTANT - Make sure you do not have any other config files under the
/etc/netplandirectory, otherwise it could cause unexpected networking issues / issues with booting up your node.
If you aren’t using the DHCP or want to add additional configuration, please refer to the netplan documentation here for additional config options.
Example
- File:
/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
Note that this is only an example of the netplan configuration file to show you how to disable the DNS search domain overriding and IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA). Do not blindly copy the entire config but rather use it as a reference for your convenience!
network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: all: match: name: en* dhcp4: yes dhcp4-overrides: use-domains: false # disable accept-ra, otherwise it will bring search domains to your /etc/resolv.conf # refs https://bugs.launchpad.net/netplan/+bug/1858503 accept-ra: false optional: trueTest and Apply Netplan
Test the Netplan config and apply via these commands.
resolvectl domainnetplan trynetplan applyresolvectl domainExpected/Example Output
root@ip-172-31-18-188:~# resolvectl domainGlobal:Link 2 (eth0): us-east-2.compute.internalroot@ip-172-31-18-188:~# netplan tryDo you want to keep these settings?
Press ENTER before the timeout to accept the new configuration
Changes will revert in 111 secondsConfiguration accepted.root@ip-172-31-18-188:~# netplan applyroot@ip-172-31-18-188:~# resolvectl domainGlobal:Link 2 (eth0): us-east-2.compute.internalSTEP 2 - Kubernetes Configurations
Create Provider namespaces on your Kubernetes cluster.
Run these commands from a Kubernetes control plane node which has kubectl access to cluster.
kubectl create ns akash-serviceskubectl label ns akash-services akash.network/name=akash-services akash.network=true
kubectl create ns leasekubectl label ns lease akash.network=trueSTEP 3 - Export Provider Wallet
In this section we will export the pre-existing, funded wallet to store the private key in a local file. To conduct the commands in this section the Akash CLI must be installed which is detailed in this guide (STEP 1 only).
The wallet used will be used for the following purposes:
- Pay for provider transaction gas fees
- Pay for bid collateral which is discussed further in this section
Make sure to create a new Akash account for the provider and do not reuse an account used for deployment purposes. Bids will not be generated from your provider if the deployment orders are created with the same key as the provider.
List Available Keys
- Print the key names available in the local OS keychain for use in the subsequent step
provider-services keys listExample/Expected Output
NOTE - in this example the provider key name is
defaultand this key name will be used in the subsequent sections of this documentation. Please adjust the key nane as necessary to suit your needs and preferences.
provider-services keys list- name: "" type: local address: akash1<redacted> pubkey: '{"@type":"/cosmos.crypto.secp256k1.PubKey","key":"<redacted>"}' mnemonic: ""- name: default type: local address: akash1<redacted> pubkey: '{"@type":"/cosmos.crypto.secp256k1.PubKey","key":"<redacted>"}' mnemonic: ""Export Private Key to Local File
- The key-name can be any name of your choice
- Note the passphrase used to protect the private key as it will be used in future steps
NOTE - The passhprase MUST be at least 8 characters long. Otherwise provider will encounter
failed to decrypt private key: ciphertext decryption failed errorwhenkeys importis executed.
STEP 1 - Export Provider Key
cd ~
provider-services keys export defaultExpected/Example Output
provider-services keys export default
Enter passphrase to encrypt the exported key:Enter keyring passphrase:-----BEGIN TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----kdf: bcryptsalt: REDACTEDtype: secp256k1
REDACTED-----END TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----STEP 2 - Create key.pem and Copy Output Into File
- Create a
key.pemfile
cd ~
vim key.pem- Copy the output of the prior command (
provider-services keys export default) into thekey.pemfile
NOTE - file should contain only what’s between
-----BEGIN TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----and-----END TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----(including theBEGINandENDlines):
Example/Expected File Contents
cat key.pem-----BEGIN TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----kdf: bcryptsalt: REDACTEDtype: secp256k1
REDACTED-----END TENDERMINT PRIVATE KEY-----STEP 4 - Helm Installation on Kubernetes Node
Install Helm on a Kubernetes Master Node
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.11.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf helm-v3.11.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
install linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
###Remove any potential prior repo instanceshelm repo remove akash
helm repo add akash https://akash-network.github.io/helm-chartsConfirmation of Helm Install
Print Helm Version
helm versionExpected Output
# helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.11.0", GitCommit:"472c5736ab01133de504a826bd9ee12cbe4e7904", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.18.10"}Step 5 - Domain Name Review
Overview
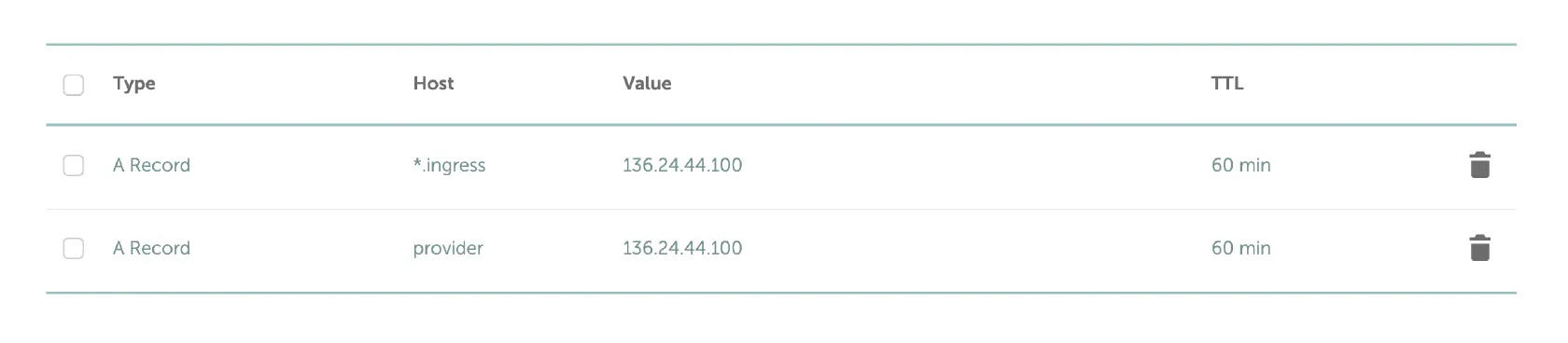
Add DNS (type A) records for your Akash Provider related domains on your DNS hosting provider.
Akash Provider Domain Records
- Replace yourdomain.com with your own domain name
- DNS (type A) records should point to public IP address of a single Kubernetes worker node of your choice
*.ingress.yourdomain.com
provider.yourdomain.comNOTE - do not use Cloudflare or any other TLS proxy solution for your Provider DNS A records.
NOTE - Instead of the multiple DNS A records for worker nodes, consider using CNAME DNS records such as the example provided below. CNAME use allows ease of management and introduces higher availability.
*.ingress 300 IN CNAME nodes.yourdomain.com.
nodes 300 IN A x.x.x.x
nodes 300 IN A x.x.x.x
nodes 300 IN A x.x.x.x
provider 300 IN CNAME nodes.yourdomain.com.
Example DNS Configuration
Step 6 - Hostname Operator Build
- Run the following command to build the Kubernetes hostname operator
- Note - if a need arises to use a different software version other than the one defined in the Chart.yaml Helm file - include the following switch. In most circumstances this should not be necessary.
--set image.tag=<image-name>- Example:
--set image.tag=0.1.0
helm install akash-hostname-operator akash/akash-hostname-operator -n akash-servicesExpected/Example Output
NAME: akash-hostname-operatorLAST DEPLOYED: Thu Apr 28 19:06:30 2022NAMESPACE: akash-servicesSTATUS: deployedREVISION: 1TEST SUITE: NoneNOTES:1. Get the application URL by running these commands: export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace akash-services -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=hostname-operator,app.kubernetes.io/instance=hostname-operator" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") export CONTAINER_PORT=$(kubectl get pod --namespace akash-services $POD_NAME -o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}") echo "Visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 to use your application" kubectl --namespace akash-services port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:$CONTAINER_PORTHostname Operator Confirmation
kubectl get pods -n akash-servicesExpected output (pod mame will differ)
root@node1:~# kubectl get pods -n akash-services
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEakash-hostname-operator-84977c6fd9-qvnsm 1/1 Running 0 3m29sSTEP 7 - Inventory Operator Install
NOTE - the Inventory Operator is now required on ALL Akash Providers. Previously this operator was only required when the Provider hosted persistent storage. But the operator is now mandated on all providers.
helm install inventory-operator akash/akash-inventory-operator -n akash-servicesExpected Output
root@node1:~/helm-charts/charts# helm install inventory-operator akash/akash-inventory-operator -n akash-services
NAME: inventory-operatorLAST DEPLOYED: Thu May 5 18:15:57 2022NAMESPACE: akash-servicesSTATUS: deployedREVISION: 1TEST SUITE: NoneInventory Operator Confirmation
kubectl get pods -n akash-services -o wideExpected output (pod names will differ)
NOTE - a pod should exist for the Inentory Operator itself (I.e.
operator-inventory-7d97d54b7f-sjz5vin the example below) and one Hardware Discovery pod per Kubernetes host.
root@node1:~# kubectl get pods -n akash-services -o wideNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATESoperator-hostname-84875c8df7-rzfct 1/1 Running 0 4m31s 10.233.71.2 node3 <none> <none>operator-inventory-7d97d54b7f-sjz5v 1/1 Running 0 3m54s 10.233.75.2 node2 <none> <none>operator-inventory-hardware-discovery-node1 1/1 Running 0 3m49s 10.233.102.131 node1 <none> <none>operator-inventory-hardware-discovery-node2 1/1 Running 0 3m49s 10.233.75.3 node2 <none> <none>operator-inventory-hardware-discovery-node3 1/1 Running 0 3m49s 10.233.71.3 node3 <none> <none>STEP 8 - Provider Build via Helm Chart
Overview
In this section the Akash Provider will be installed and customized via the use of Helm Charts.
NOTE - when the Helm Chart is installed the Provider instance/details will be created on the blockchain and your provider will be registered in the Akash open cloud marketplace. The associated transaction for Provider creation is detailed here.
Environment Variables
- Declare the following environment variables for Helm use
- Replace the variables with your own settings
- Set akash provider address that starts with
akash1
This allows the akash-provider to decrypt the key
export ACCOUNT_ADDRESS=akash1XXXX2. Set the password you have entered upon akash keys export > key.pem
export KEY_PASSWORD='12341234'3. Set your domain. Register DNS A and wildcard address as specified in previous step, i.e. provider.test.com DNS A record and *.ingress.test.com DNS wildcard record.
Domain should be a publicly accessible DNS name dedicated for your provider use such as test.com.
The domain specified in this variable will be used by Helm during the Provider chart install process to produce the “provider.yourdomain.com” sub-domain name and the “ingress.yourdomain.com” sub-domain name. The domain specified will also be used by Helm during the Ingress Controller install steps coming up in this guide. Once your provider is up and running the *.ingress.yourdomain.com URI will be used for web app deployments such as abc123.ingress.yourdomain.com.
export DOMAIN=test.com4. Set the Akash RPC node for your provider to use
- If you are going to deploy Akash RPC Node using Helm-Charts then set the node to http://akash-node-1:26657 It is recommended that you install your own Akash RPC node. Follow this guide to do so.
Ensure that the RPC node utilized is in sync prior to proceeding with the provider build.
NOTE - in the example provided below the NODE variable is set toakash-node-1which is the Kubernetes service name of the RPC node when installed via Helm. Usekubectl get svc -n akash-servicesto confirm the service name and status.
export NODE=http://akash-node-1:26657Provider Withdraw Period
- Akash providers may dictate how often they withdraw funds consumed by active deployments/tenants escrow accounts
- Few things to consider regarding the provider withdraw period:
- The default withdraw setting in the Helm Charts is one (1) hour
- An advantage of the one hour default setting is assurance that a deployment may not breach the escrow account dramatically. If the withdraw period were set to 12 hours instead - the deployment could exhaust the amount in escrow in one hour (for example) but the provider would not calculate this until many hours later and the deployment would essentially operate for free in the interim.
- A disadvantage of frequent withdraws is the possibility of losing profitability based on fees incurred by the providers withdraw transactions. If the provider hosts primarily low resource workloads, it is very possible that fees could exceed deployment cost/profit.
OPTIONAL - Update the Provider Withdraw Period
- If it is desired to change the withdrawal period from the default one hour setting, update the
withdrawalperiodsetting in the provider.yaml file created subsequently in this section. - In the example the Provider Build section of this doc the withdrawal period has been set to 12 hours. Please adjust as preferred.
Provider Build Prep
- Ensure you are applying the latest version of subsequent Helm Charts install/upgrade steps
helm repo updateCreate a provider.yaml File
- Issue the following command to build your Akash Provider
- Update the following keys for your unique use case
regionorganization
- Optional Parameters - the following parameters may be added at the same level as
fromandkeyif you which to advertise your support email address and company website URL. (NOTE: These are not “attributes” but rather informational fields; add them as in the example below)emailwebsite
cd ~
mkdir provider
cd provider
cat > provider.yaml << EOF---from: "$ACCOUNT_ADDRESS"key: "$(cat ~/key.pem | openssl base64 -A)"keysecret: "$(echo $KEY_PASSWORD | openssl base64 -A)"domain: "$DOMAIN"node: "$NODE"withdrawalperiod: 12hattributes: - key: region value: "<YOUR REGION>" # set your region here, e.g. "us-west" - key: host value: akash - key: tier value: community - key: organization value: "<YOUR ORG>" # set your organization name hereemail: <YOUR EMAIL> # set your email herewebsite: <YOUR SITE> # set your website (if you have)EOFExample provider.yaml File Creation
root@linux-server ~ % cat > provider.yaml << EOF---from: "$ACCOUNT_ADDRESS"key: "$(cat ~/key.pem | openssl base64 -A)"keysecret: "$(echo $KEY_PASSWORD | openssl base64 -A)"domain: "$DOMAIN"node: "$NODE"withdrawalperiod: 12hattributes: - key: region value: us-east - key: host value: akash - key: tier value: community - key: organization value: myorganizationemail: your@email.comwebsite: yoursite.comEOFVerification of provider.yaml File
- Issue the following commands to verify the
provider.yamlfile created in previous steps
cd ~/provider
cat provider.yamlExample provider.yaml Verification Output
- Ensure there are no empty values
from: akash1<REDACTED>key: LS0tLS1CRU<REDACTED>0tLS0tCg==keysecret: QUtB<REDACTED>XIKdomain: test.comnode: http://<rpc-address>:26657withdrawalperiod: 12hattributes:- key: region value: us-east- key: host value: akash- key: tier value: community- key: organization value: mycompanyemail: your@email.comwebsite: yoursite.comProvider Bid Defaults
- When a provider is created the default bid engine settings are used. If desired these settings could be updated and added to the
provider.yamlfile. But we would recommend initially using the default values. - Note - the
bidpricestoragescalevalue will get overridden by-f provider-storage.yamlcovered in Provider Persistent Storage documentation. - Note - if you want to use a shellScript bid price strategy, pass the bid price script via
bidpricescriptvariable detailed in the bid pricing script doc. This will automatically suppress allbidprice<cpu|memory|endpoint|storage>scalesettings.
bidpricecpuscale: "0.004" # cpu pricing scale in uakt per millicpubidpricememoryscale: "0.0016" # memory pricing scale in uakt per megabytebidpriceendpointscale: "0" # endpoint pricing scale in uakt per endpointbidpricestoragescale: "0.00016" # storage pricing scale in uakt per megabyteProvider CRD Installations
- Kubernetes CRDs are no longer delivered by the Helm as of chart
v4.3.0. - CRDs are now installed manually using this step.
NOTE - You do not need to run this command if you previously installed the Akash Provider and are now performing an upgrade.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/akash-network/provider/v0.6.4/pkg/apis/akash.network/crd.yamlInstall the Provider Helm Chart
helm install akash-provider akash/provider -n akash-services -f provider.yamlExpected Output of Provider Helm Install
NAME: akash-providerLAST DEPLOYED: Thu Apr 28 18:58:10 2022NAMESPACE: akash-servicesSTATUS: deployedREVISION: 1TEST SUITE: NoneProvider Confirmation
kubectl get pods -n akash-servicesExpected output (example and name following akash-provider will differ)
root@node1:~# kubectl get pods -n akash-services
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEakash-provider-6d7c455dfb-qkf5z 1/1 Running 0 4m37sTroubleshooting
If your Akash Provider pod status displays init:0/1 for a prolonged period of time, use the following command to view Init container logs. Often the Provider may have a RPC issue and this should be revealed in these logs. RPC issues may be caused by an incorrect declaration in the NODE variable declaration issued previously in this section. Or possibly your custom RPC node is not in sync.
kubectl -n akash-services logs -l app=akash-provider -c init --tail 200 -fHelm Chart Uninstall Process
- Should a need arise to uninstall the Helm Chart and attempt the process anew, the following step can be used
- Only conduct this step if there is a problem with Akash Provider Helm Chart install
- This Helm uninstall technique can be used for this or any subsequent chart installs
- Following this step - if needed - start the Provider Helm Chart install anew via the prior step in this page
helm uninstall akash-provider -n akash-servicesSTEP 9 - Provider Bid Customization
Overview
NOTE - if you are updating your provider bid script from a previous version use this bid script migration guide.
- If there is a desire to manipulate the provider bid engine, include the
--set bidpricescriptswitch . The pricing script used in this switch is detailed in the Akash Provider Bid Pricing section of this guide. - Note - When the provider deployment is created the bid script should return the price in under 5 seconds . If the script does not execute in this time period the following error message will be seen in the provider pod logs. Such a report would suggest that there is an error/issue with script customizations that should be reviewed. Following review and adjustment, uninstall the provider deployment (via helm uninstall) and reinstall.
- Note - there is further discussion on the bid script and deployer address whitelisting in this section.
USDC Stable Payment Support - note that the current, default bid script enables stable payment support on the Akash Provider. Akash deployments using stable payments are taxed at a slightly higher rate than deployments using AKT payment. If you choose not to support stable payments on your provider, remove stable payment support from the default bid script.
Provider Bid Script Customization Steps
STEP 1 - Update provider.yaml File
- If customization of your provider bid pricing is desired, begin by updating the
provider.yamlfile which will be used to hold customized values
cd ~/provider
vim provider.yamlSTEP 2 - Customize the provider.yaml File
Update your
provider.yamlfile with the price targets you want. If you don’t specify these keys, the bid price script will default values shown below
price_target_gpu_mappings sets the GPU price in the following way and in the example provided:
a100nvidia models will be charged by120USD/GPU unit a montht4nvidia models will be charged by80USD/GPU unit a month- Unspecified nvidia models will be charged
130USD/GPU unit a month (if*is not explicitly set in the mapping it will default to100USD/GPU unit a month) - Extend with more models your provider is offering if necessary with syntax of
<model>=<USD/GPU unit a month>
price_target_cpu: 1.60price_target_memory: 0.80price_target_hd_ephemeral: 0.02price_target_hd_pers_hdd: 0.01price_target_hd_pers_ssd: 0.03price_target_hd_pers_nvme: 0.04price_target_endpoint: 0.05price_target_ip: 5price_target_gpu_mappings: "a100=120,t4=80,*=130"STEP 3 - Download Bid Price Script
cd ~/provider
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/akash-network/helm-charts/main/charts/akash-provider/scripts/price_script_generic.shSTEP 4 - Upgrade akash-provider Deployment with Customized Bid Script
helm upgrade akash-provider akash/provider -n akash-services -f provider.yaml --set bidpricescript="$(cat price_script_generic.sh | openssl base64 -A)"Verification of Bid Script Update
helm list -n akash-services | grep akash-providerExpected/Example Output
# helm list -n akash-services | grep akash-providerakash-provider akash-services 28 2023-09-19 12:25:33.880309778 +0000 UTC deployed provider-6.0.5 0.4.6STEP 10 - Ingress Controller Install
Create Upstream Ingress-Nginx Config
Create the ingress-nginx-custom.yaml file via this step
NOTE - in the default install the dedicated Akash RPC Node used for your provider is reachable only within the Kubernetes cluster. This is done intentionally as this RPC Node is intended for use only by the Akash Provider only. The Provider will have access within the cluster to the RPC Node. This additionally protects the RPC Node from possible DDoS attacks from external parties. If have a need to expose the Provider’s RPC Node to the outside world, use the
ingress-nginx-custom.yamlfile included in this section instead.
cd ~
cat > ingress-nginx-custom.yaml << EOFcontroller: service: type: ClusterIP ingressClassResource: name: "akash-ingress-class" kind: DaemonSet hostPort: enabled: true admissionWebhooks: port: 7443 config: allow-snippet-annotations: false compute-full-forwarded-for: true proxy-buffer-size: "16k" metrics: enabled: true extraArgs: enable-ssl-passthrough: truetcp: "8443": "akash-services/akash-provider:8443" "8444": "akash-services/akash-provider:8444"EOFExpose RPC Node to Outside World
Use this step only if you choose to expose your Akash Provider RPC Node to the outside world
cd ~
cat > ingress-nginx-custom.yaml << EOFcontroller: service: type: ClusterIP ingressClassResource: name: "akash-ingress-class" kind: DaemonSet hostPort: enabled: true admissionWebhooks: port: 7443 config: allow-snippet-annotations: false compute-full-forwarded-for: true proxy-buffer-size: "16k" metrics: enabled: true extraArgs: enable-ssl-passthrough: truetcp: "1317": "akash-services/akash-node-1:1317" "8443": "akash-services/akash-provider:8443" "8444": "akash-services/akash-provider:8444" "9090": "akash-services/akash-node-1:9090" "26656": "akash-services/akash-node-1:26656" "26657": "akash-services/akash-node-1:26657"EOFInstall Upstream Ingress-Nginx
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx \ --version 4.11.3 \ --namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace \ -f ingress-nginx-custom.yamlApply Necessary Labels
- Label the
ingress-nginxnamespace and theakash-ingress-classingressclass
kubectl label ns ingress-nginx app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx app.kubernetes.io/instance=ingress-nginx
kubectl label ingressclass akash-ingress-class akash.network=trueStep 11 - Firewall Rule Review
External/Internet Firewall Rules
The following firewall rules are applicable to internet-facing Kubernetes components.
Akash Provider
8443/tcp - for manifest uploadsIngress Controller
80/tcp - for web app deployments443/tcp - for web app deployments30000-32767/tcp - for Kubernetes node port range for deployments30000-32767/udp - for Kubernetes node port range for deploymentsStep 12 - Disable Unattended Upgrades
Overview
Unattended upgrades can bring all sorts of uncertainty/troubles such as updates of NVIDIA drivers and have the potential to affects your Provider/K8s cluster. Impact of unattended upgrades can include:
nvidia-smiwill hang on the host/podnvdp pluginwill become stuck and hence K8s cluster will run in a non-desired state where closed deployments will be stuck inTerminatingstatus
Disable Unattended Upgrades
To disable unattended upgrades, execute these two commands on your Kubernetes worker & control plane nodes:\
echo -en 'APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "0";\nAPT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";\n' | tee /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
apt remove unattended-upgrades
systemctl stop unattended-upgrades.servicesystemctl mask unattended-upgrades.serviceVerify
These commands should output 0 following the disable of unattended upgrades. Conduct these verifications your Kubernetes worker & control plane nodes:
apt-config dump APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade
apt-config dump APT::Periodic::Update-Package-ListsExample/Expected Output
# apt-config dump APT::Periodic::Unattended-UpgradeAPT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";
# apt-config dump APT::Periodic::Update-Package-ListsAPT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "0";STEP 13 - Provider Whitelisting (Optional)
Overview
- Akash Provider deployment address Whitelist functionality is now enabled in the bid price script
- To use it simply specify the list via whitelist_url attribute as detailed in this section
- Complete the steps in this section to enable/customize Akash Provider Whitelisting
Update the Akash Helm-Charts Repo
helm repo update akashVerify Akash/Provider Helm Chart is 4.3.4 Version or Higher
helm search repo akash/providerExpected/Example Output
# helm search repo akash/providerNAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTIONakash/provider 4.3.4 0.4.6 Installs an Akash provider (required)Download Bid Price Script Which Supports Whitelisting
USDC Stable Payment Support - note that the current, default bid script downloaded in this step enables stable payment support on the Akash Provider. Akash deployments using stable payments are taxed at a slightly higher rate than deployments using AKT payment. If you choose not to support stable payments on your provider, remove stable payment support from the default bid script.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/akash-network/helm-charts/main/charts/akash-provider/scripts/price_script_generic.shPrepare the Whitelist
- Example whitelist hosted on GitHub Gist can be found here
Specify the Bid Price Script and Whitelist URL
NOTE - Whitelist will only work when
bidpricescriptis also set.
NOTE - You need to specify the direct link to the whitelit (with Github Gist you need to click Raw button to get it)
helm upgrade --install akash-provider akash/provider -n akash-services -f provider.yaml \--set bidpricescript="$(cat /root/provider/price_script_generic.sh | openssl base64 -A)" \--set whitelist_url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/andy108369/1fa6cfa81674bce438a450d6c14395ea/raw/9181887be8e3e019b58e5dc8e7fce4ae0a66eeec/whitelist.txtSTEP 14 - Extras
Force New ReplicaSet Workaround
A known issue exists which occurs when a deployment update is attempted and fails due to the provider being out of resources. This is happens because K8s won’t destroy an old pod instance until it ensures the new one has been created.
Follow the steps in the Force New ReplicaSet Workaround document to address this issue.
Kill Zombie Processes
A known issue exists which occurs when a tenant creates a deployment which doesn’t handle child processes properly, leaving the defunct (aka zombie) proceses behind. These could potentially occupy all available process slots.
Follow the steps in the Kill Zombie Processes document to address this issue.